Improve toddler nutrition with our comprehensive guide. Expert tips on balanced diets, managing picky eaters, and more.

Toddler nutrition is a critical aspect of early childhood development. According to the research, proper nutrition during the early years can have long-term impacts on a child’s growth, development, and overall health.
Did you know that nearly 1 in 5 children in the United States is obese by the time they reach kindergarten? This alarming statistic underscores the importance of establishing healthy eating habits early on.
In this comprehensive guide, we will delve into the intricacies of toddler nutrition, providing you with expert tips and practical strategies to ensure your toddler gets the best possible start in life.
Section 1: Understanding Toddler Nutrition

Nutritional Needs
At the core of toddler nutrition are the specific nutritional needs that support rapid growth and development. Toddlers require a balanced intake of macronutrients—proteins, fats, and carbohydrates—as well as essential vitamins and minerals. According to the American Academy of Pediatrics (AAP), toddlers should consume about 1,000 to 1,400 calories per day, depending on their activity level and growth needs (AAP, 2021).
Proteins are vital for muscle development and repair. Sources include lean meats, eggs, dairy products, and plant-based options like beans and lentils. Fats are crucial for brain development, with healthy fats found in avocados, nuts, and olive oil. Carbohydrates provide the primary energy source, ideally from whole grains, fruits, and vegetables.
Common Deficiencies
Understanding common nutritional deficiencies can help parents proactively address potential gaps in their toddler’s diet. Iron deficiency, for instance, is prevalent among toddlers and can lead to anemia, impacting cognitive and physical development. The CDC recommends incorporating iron-rich foods like lean meats, fortified cereals, and leafy greens to combat this (CDC, 2020).
Another common deficiency is vitamin D, essential for bone health. The AAP advises ensuring sufficient vitamin D intake through fortified milk and sunlight exposure (AAP, 2018). Calcium, crucial for bone development, should come from dairy products or fortified plant-based alternatives.
Balanced Diet
A balanced diet for toddlers includes a variety of foods from all food groups, ensuring they get a range of nutrients. The MyPlate model by the USDA is an excellent guideline, suggesting that half the plate be fruits and vegetables, one-quarter of grains, and one-quarter of protein, with a serving of dairy on the side (USDA, 2021). This approach helps parents plan meals that are not only nutritious but also visually appealing to toddlers.
Section 2: Creating a Balanced Diet Plan

Meal Planning Tips
Effective meal planning can simplify the process of providing balanced nutrition. Start by incorporating a variety of foods to ensure a wide range of nutrients. Planning meals ahead of time can help maintain balance and prevent last-minute unhealthy choices. Using a weekly meal planner can be particularly helpful.
Portion Sizes
Understanding portion sizes is crucial in toddler nutrition. The USDA provides guidelines suggesting that portions should be about one-quarter to one-third of an adult portion. For instance, a serving of meat for a toddler should be about the size of their palm, and fruits and vegetables should be about half a cup each.
Food Groups
A balanced diet for toddlers should include a variety of foods from all essential food groups:
- Fruits and Vegetables: These should occupy half of your toddler’s plate. Strive for a colorful assortment to ensure a broad spectrum of vitamins and minerals.
- Proteins: Incorporate sources like lean meats, fish, eggs, beans, and nuts. Protein is vital for the development of muscles and tissues.
- Grains: Prefer whole grains like oatmeal, brown rice, and whole wheat bread over refined grains to provide more fiber and nutrients.
- Dairy: Offer milk, cheese, and yogurt to supply calcium and vitamin D for bone health.
Section 3: Practical Tips for Improving Toddler Nutrition
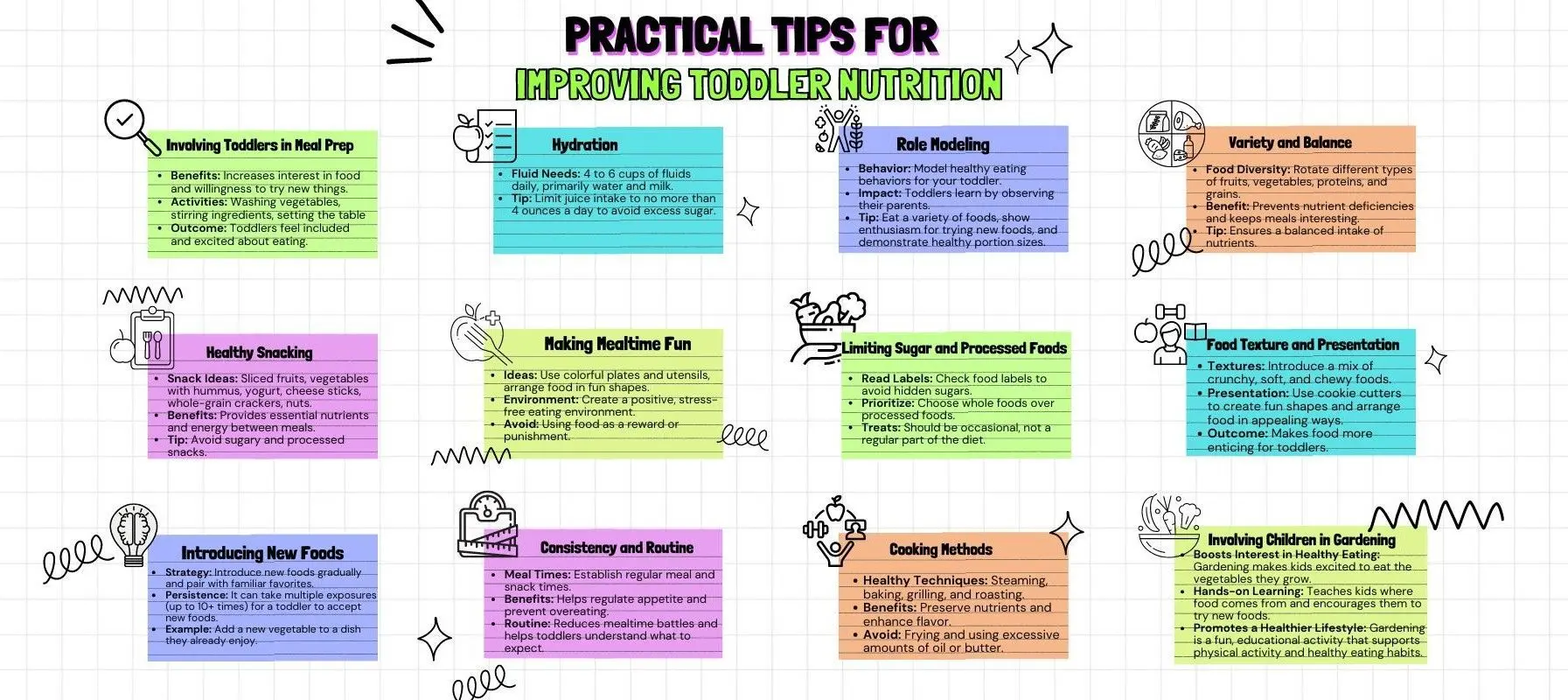
Involving Toddlers in Meal Prep
Getting toddlers involved in meal preparation can increase their interest in food and their willingness to try new things. Simple tasks like washing vegetables, stirring ingredients, or setting the table can make them feel included and more excited about eating what they’ve helped create.

Healthy Snacking
Snacks are an essential part of toddler nutrition, providing additional nutrients and energy throughout the day. Opt for healthy snacks like sliced fruits, and vegetables with hummus, yogurt, and whole-grain crackers. Avoid sugary snacks and processed foods, which can contribute to poor eating habits.
Introducing New Foods
Introducing new foods can be challenging, especially with picky eaters. The key is persistence and patience. It can take multiple exposures—up to 10 or more times—for a toddler to accept a new food. Pairing new foods with familiar favorites can make the process smoother. For example, add a new vegetable to a dish they already enjoy.
Hydration
Proper hydration is often overlooked in toddler nutrition. Toddlers should drink about 4 to 6 cups of fluids per day, primarily water and milk. Limit juice intake to no more than 4 ounces a day, as it can be high in sugar and low in essential nutrients.
Making Mealtime Fun
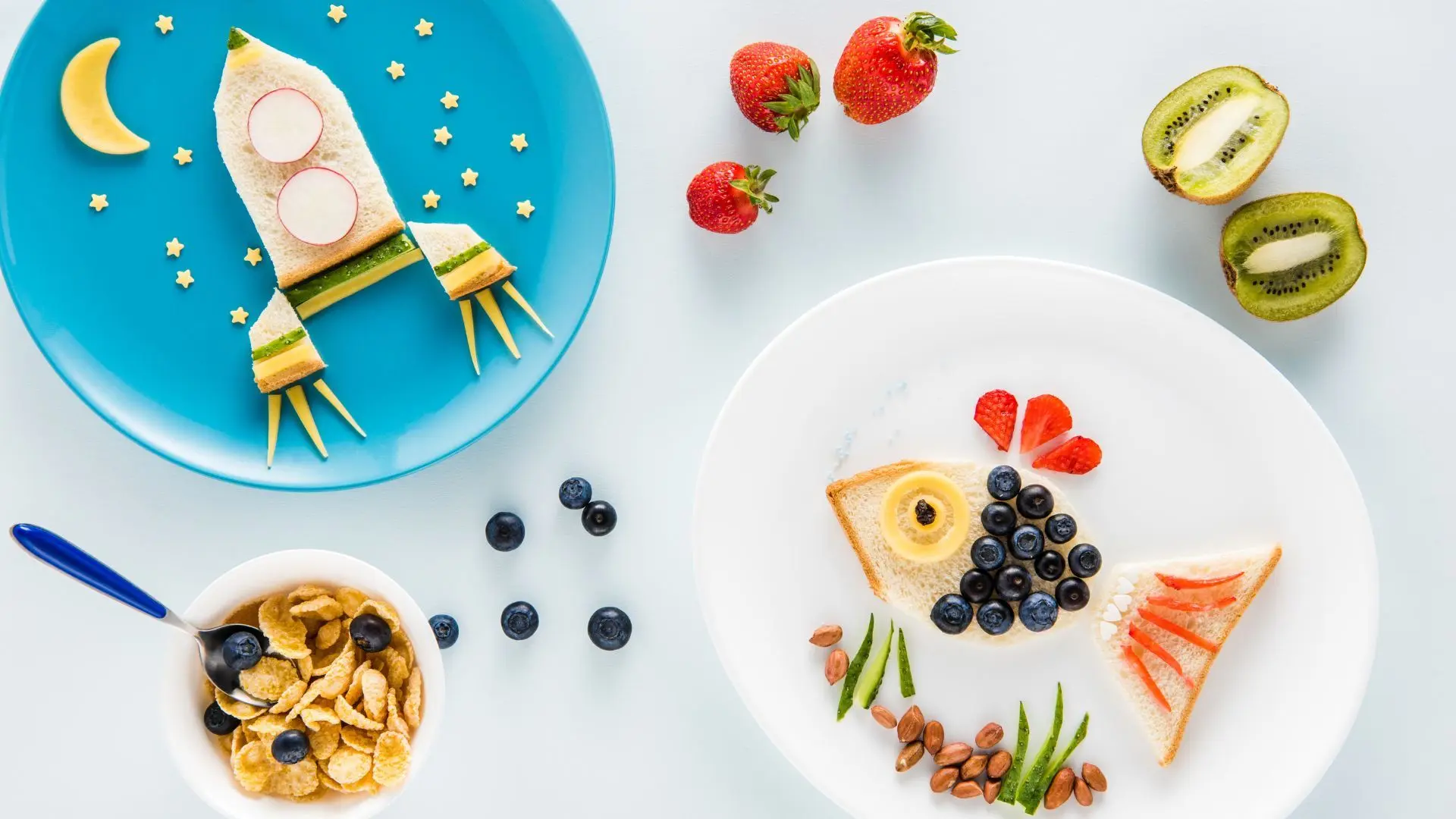
Making mealtime enjoyable can encourage better eating habits. Use colorful plates and utensils, arrange food in fun shapes, and create a positive, stress-free eating environment. Avoid making food a reward or punishment, as this can create unhealthy attitudes toward eating.

Consistency and Routine
Consistency and routine are crucial for toddlers. Establish regular meal and snack times to help regulate their appetite and prevent overeating. Consistent routines also help toddlers understand what to expect and reduce mealtime battles.
Role Modeling
Toddlers learn by observing their parents. By modeling healthy eating behaviors, you set a positive example. Eat a variety of foods, express enthusiasm about trying new foods, and demonstrate healthy portion sizes.
Limiting Sugar and Processed Foods
High sugar and processed foods can negatively impact toddler nutrition and lead to poor eating habits. Read food labels to avoid hidden sugars and prioritize whole foods. Treats should be occasional, not a regular part of the diet.
Cooking Methods
Healthy cooking methods can preserve nutrients and make meals more appealing. Steaming, baking, grilling, and roasting are excellent techniques to enhance the flavor and retain the nutritional value of food. Avoid frying and using excessive amounts of oil or butter.
Variety and Balance
Offering a variety of foods ensures a balanced intake of nutrients. Rotate different types of fruits, vegetables, proteins, and grains to keep meals interesting and nutritionally diverse offering a diverse range of foods helps ensure your toddler receives all necessary nutrients and supports their overall well-being.
Food Texture and Presentation
Different textures and appealing presentations can make food more enticing for toddlers. Introduce a mix of crunchy, soft, and chewy foods to keep meals interesting. Use cookie cutters to create fun shapes and arrange food in visually appealing ways.
Involving Children in Gardening
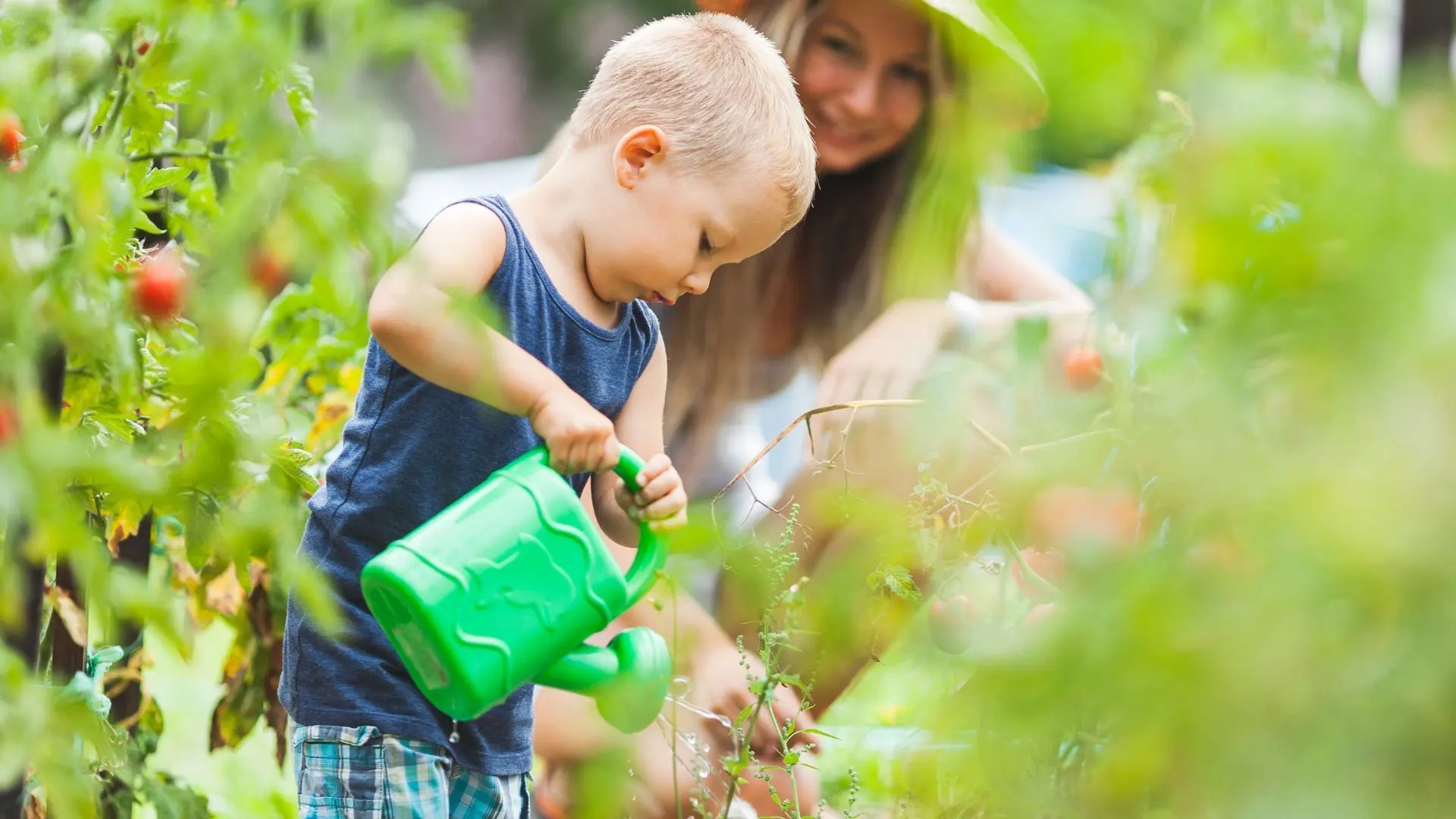

Engaging children in gardening can significantly improve their interest in healthy eating. When children participate in growing their own vegetables, they are more likely to be excited about eating them. This hands-on experience not only teaches them about where food comes from but also encourages them to try new foods. Plus, gardening can be a fun and educational family activity that promotes a healthier lifestyle.
Section 4: Addressing Common Challenges
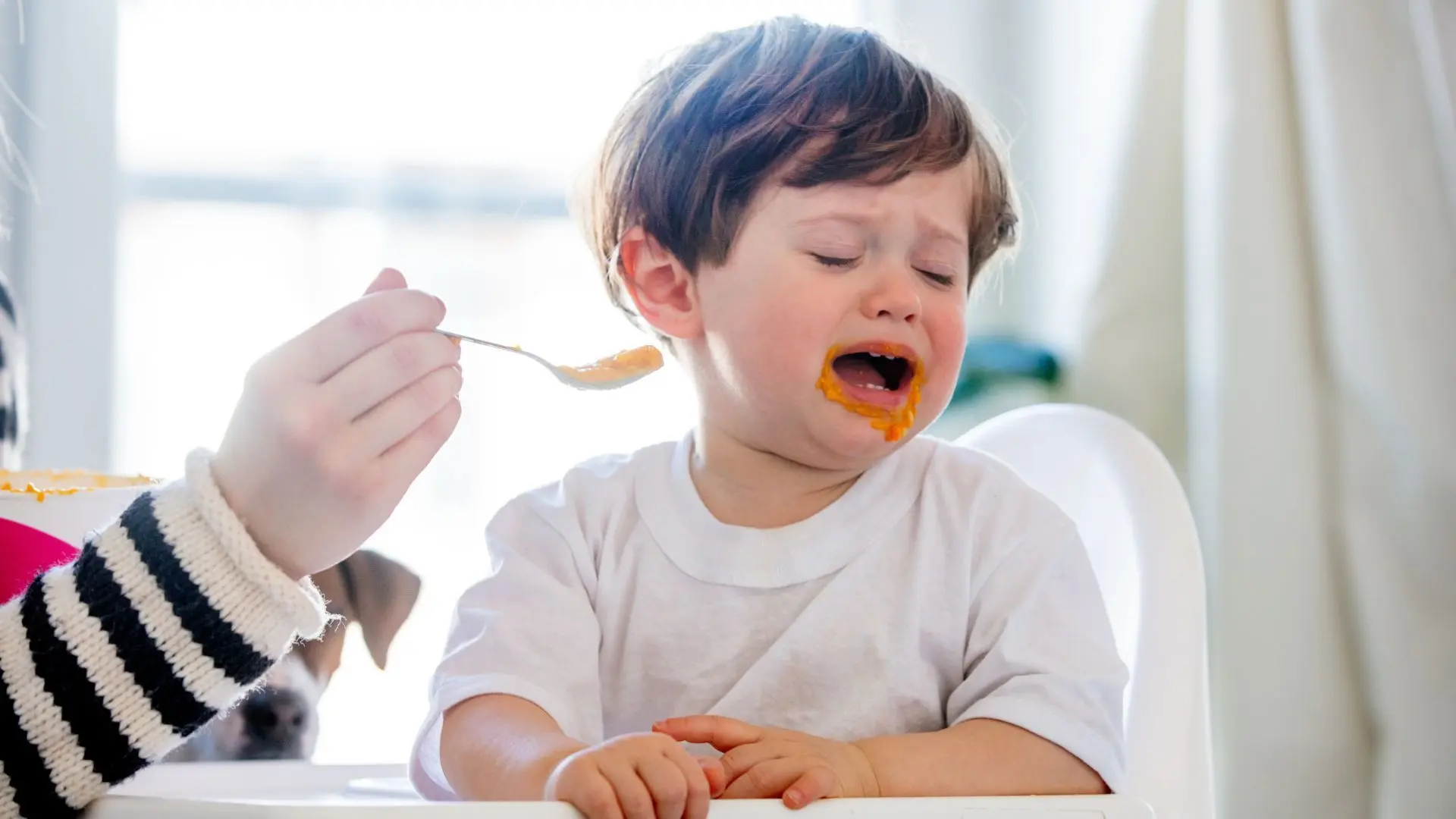

Dealing with Picky Eaters
Picky eating is a common issue in toddler nutrition. To address this, offer a variety of foods without pressuring your child to eat. Keep introducing rejected foods in different forms and pair them with favorites. Celebrate small victories and remain patient.
Managing Food Allergies
Managing food allergies while ensuring proper nutrition can be challenging. Work with a pediatrician or a registered dietitian to identify safe food alternatives and ensure a balanced diet. Keep a food diary to track any reactions and avoid cross-contamination..
Avoiding Junk Food
Limiting junk food is essential for maintaining healthy eating habits. Stock your pantry with healthy options and reduce the availability of sugary snacks and drinks. Educate your toddler about the benefits of healthy eating in a way they can understand.
Section 5: Expert Tips and Tricks
Advice from Nutritionists
Nutritionists emphasize the importance of whole foods and a balanced diet in toddler nutrition. Dr. Sarah Johnson, a pediatric nutritionist, advises incorporating a rainbow of fruits and vegetables to ensure a variety of nutrients. She also suggests involving toddlers in meal prep to increase their interest in healthy foods.
Educational Resources
Numerous resources are available for parents looking to improve their knowledge of toddler nutrition. Books like “Child of Mine: Feeding with Love and Good Sense” by Ellyn Satter and websites like ChooseMyPlate.gov provide valuable information and practical tips.
Meal Prep Shortcuts
Busy parents can benefit from meal prep shortcuts. Batch cooking and freezing meals can save time and ensure that nutritious options are always available. Pre-chopping vegetables and preparing snack packs can also make healthy eating more convenient.

Shopping Tips
Grocery shopping for toddler nutrition can be made easier with a few tips. Stick to the perimeter of the store where fresh produce, meats, and dairy are located. Read labels to avoid added sugars and unhealthy additives. Consider buying organic for certain produce items to reduce pesticide exposure.
Understanding Food Labels
Reading food labels is essential for making healthier dietary choices. Look for items with minimal ingredients and avoid those with high sugar content or artificial additives. The FDA provides guidelines on reading nutrition labels, which can be a helpful resource for parents.
Mindful Eating
Teaching toddlers mindful eating habits can foster a healthy relationship with food. Encourage them to eat slowly, enjoy their meals, and recognize when they are full. Avoid distractions like screens during mealtime to promote mindful eating.
Incorporating Superfoods
Superfoods like blueberries, sweet potatoes, and quinoa are packed with nutrients and can be easily incorporated into a toddler’s diet. These foods provide essential vitamins and minerals that support overall health and development.
Conclusion
In summary, improving toddler nutrition involves understanding their nutritional needs, planning balanced meals, addressing common challenges, ensuring variety, and seeking expert advice. By incorporating these expert tips and tricks, you can foster healthy eating habits and support your toddler’s growth and development. Remember, consistency and patience are key. If you have any experiences, tips, or questions, please share them in the comments below. Your insights can help other parents on this journey.
You may also be interested in : 4-Year-Old Development: What to Expect and How to Support Growth